MGT 300 - CHAPTER 13
E- Business
Ø The internet is a powerful channel that
presents new opportunities for an organization to :
*Touch customer
*Enrich products and
services with information
*Reduce costs
Ø How do e-commerce and e-business differ ?
*E-commerce
– the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet (online
transactions)
*E-business
– the conducting of business on the Internet including, not only buying and
selling, but also serving customers and collaborating with business partners
(online transaction, serving customers and collaborating with business partner
)
Ø Electronic marketplace (e-marketplace)
*Electronic
marketplaces, or e-marketplaces, present structures for conducting commercial
exchange, consolidating supply chains, and creating new sales channels
*Their primary goal is
to increase market efficiency by tightening and automating the relationship
between buyers and sellers
*Existing
e-marketplaces allow access to various mechanism in which to buy and sell
almost anything, from services to direct materials
Ø Business-to-consumer (B2C)
*Common B2C e-business
models include :
-e-shop
: a version of retail store where customers can shop at any hour of the
day without leaving their home or office
-e-mail
: consists the number of e-shops; it serves as a gateway through which a
visitor can access other e-shops
*Business types :
-Brick-and-mortar
business : operates in physical store without an internet presence. Eg :
Bata
-Pure-play
business : a business that operates on the internet only without a physical
store. Eg: include fashionvalet.com
-Click-and-mortar
business : a business that operates in a physical store and on the
internet. Eg:Hijabs by Hanami
Ø Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
*Priceline.com is an
example of a C2B e-business model
*The demand for C2B
e-business will increase over the next few years due to customer’s desire for
greater convenience and lower prices
Ø Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
*Online actions
- Electronic
auction (e-auction) – sellers and buyers solicit consecutives bids from
each others and prices are determined dynamically
- Forward
auction – seller use as a selling channel to many buyers and the highest
bid wins
- Reverse
auction – buyers use to purchase a product or services, selecting the
seller with the lowest bids
*C2C communities
include :
- Communities
of interest – people interact with each other on specific topics, such as
golfing and stamp collecting
- Communities
of relations – people come together to share certain life experiences, such
as cancer patients, senior citizens and car enthusiasts
- Communities
of fantasy – people participate in imaginary environments, such as fantasy
football teams and playing one-by-one with Michael Jordan
Ø E-Business benefits
*Highly accessible
-Businesses can operate 24 hours a day, 7 days
a week, 365 days a year
*Increased customer loyalty
-Additional channels to contact, respond to,
and access customers helps contribute to consumer loyalty
*Improved information content
-In the past, customer had to order catalogs
or travel to a physical facility before they could compare price and products
attributes. Electronic catalogs and webpages presents customers with update
information in real-time about goods, services and prices
*Increased convenience
-E-business automates and improve many of the
activities that make up a buying experience
*Increased global reach
-Businesses, both small and large, can reach
new markets
*Decreased cost
-The cost of conducting business on the
internet is substantially smaller than traditional forms of business communications
Ø E-Business challenges
*Identifying Limited Market Segments
-The main challenge of e-business is the lack
of growth in some sectors due to products or services limitation
*Managing Consumer Trust
-Internet marketers must develop a trustworthy
relationship to make that initial sale and generate customer loyalty
*Ensuring Consumer Protection
-Implement Internet Security, protect from
misuse of customer information
*Managing Consumer Trust
-Companies that operates online must obey a
patchwork of rules about which customers are subject to sales tax on their
purchase and which are not
Ø There are numerous advantages and
limitation in e-business revenue modes including :
*Transaction fees
*License fees
*Subscription fees
*Value-added fees
*Advertising fees
Mashups
Ø Web mashup – a web site or web
application that uses content from more than one source to create a completely
new services.
*Application
programming interface (API) – a set of routines, protocols and tools for
building software applications
*Mashup editor – WYSIWYGs
(What You See Is What You Get ) for mashups

















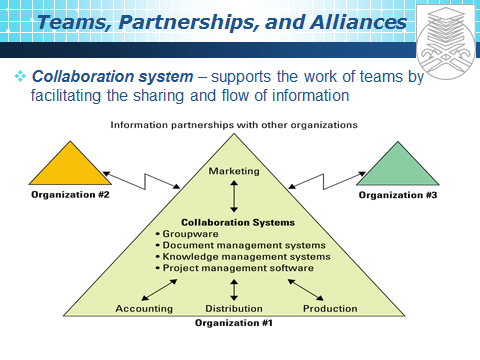
Comments
Post a Comment