MGT300 - CHAPTER 10
Extending the organization – Supply Chain Management (SCM)
- The
average company spends nearly half or every dollar that it earns on
production
- In
the past, companies focused primarily on manufacturing and quality
improvements to influences their supply chains
- The
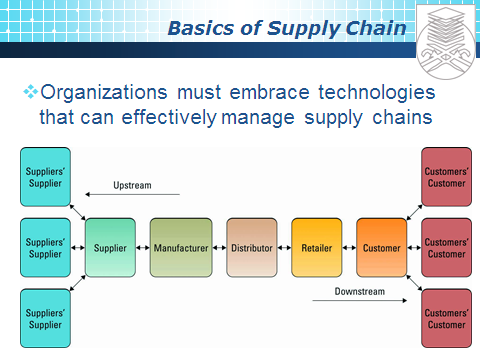
supply chain has three main links :
Ø Materials flow from suppliers and their 'upstream' suppliers at all
levels
Ø Transformation of materials into semifinished and finished products
through the organization's own production process
Ø Distribution of products to customers and their 'downstream' customers
at all levels
Ø Plan
A company must have a plan for
managing all the resources that go toward meeting customer demand for products
and services
Ø Source
Companies must carefully choose reliable
suppliers that will deliver goods and services required for making products
Ø Make
This is the step where companies
manufacture their products or services. This can include scheduling the
activities necessary for production, testing, packaging and preparing for
delivery
Ø Deliver (logistic)
Companies must be able to receive
orders from customers, fulfil their orders via a network of warehouses, pick
transportation companies to deliver the products and implement a billing and
invoicing system to facilitate payments
Ø Return
This is typically the most
problematic step in the supply chain. Companies must create a network for
receiving defective and excess products and support customers who have problems
with delivered products
Ø Visibility
More visible models of different ways to do things
in the supply chain have emerged. High visibility in the supply chain is
changing industries, as Wal-Mart demonstrated
Ø Supply chain visibility
The ability to view all areas up and down the
supply chain
Ø Bullwhip effect
Occurs when distorted product demand information
passes from one entity to the next
throughout the supply chain
Ø Supply chain visibility allows organizations to
eliminate the bullwhip effect
*To explain the bullwhip effect
to your student discuss a product that demand does not change, such as diapers.
The need for diapers is constant, it does not increase in Christmas or in the
summer, diaper are in demand all year long. The number of newborn babies
determines diaper demands, and that number is constant.
*Retailers order diapers from
distributors when their inventory level falls below a certain level, they might
order a few extra just to be safe
*Distributors order diapers from
manufactures when their inventory level falls below a certain level, they might
order a few extra just to be safe
*Manufacturers orders diapers
from suppliers when their inventory levels below a certain level, they might
order a few extra just to be safe
*Eventually the one or two extra
boxes are ordered from a few retailers becomes several thousand boxes for the
manufacturer. This is the bullwhip effect, a small ripple at one end makes a
large waves at the other end of the whip
Ø Consumer behaviour
*Companies can respond faster and
more effectively to consumer demands through supply chain enhances
*Once an organization understands
customers demand and its effect on the supply chain it can begin to estimate
the impact that its supply chain will have on its customers and ultimately the
organization performance
*Demand planning software –
generates demand forecast using statistical tools and forecasting techniques
Ø Competition
*Supply chain planning
software(SCP) – uses advanced mathematical algorithm to improve the flow and
efficiency of the supply chain
*Supply chain execution software
(SCE) – automates the different step and stages of the supply chain
*SCP and SCE both increase a
company‘s ability to compete
*SCP depends entirely on
information for its accuracy
*SCE can be as simple as
electronically routing orders from a manufacturer to a supplier
Ø Supply chain management success factors
*Make the sales to suppliers
*Wean employees off traditional
business practices
*Ensure the SCM system supports
the organizational goals
*Deploy the incremental phases
and measure and communicate success
Ø DSSs allows managers to examine performance and relationship over the supply chain and among:
*suppliers
*manufacturers
*distributors









Comments
Post a Comment